Concepts
To provision, or change modes, create a goal configuration which will take effect after a system reboot. Goals specify which operating mode the modules are to be used in. The goal is stored on the persistent memory modules for the BIOS to read on the next reboot.
A region, or interleaved set, is a grouping of one or more persistent memory modules. Regions can be created as either non-interleaved, meaning one region per persistent memory module, or interleaved, which creates one large region over all modules in a CPU socket.

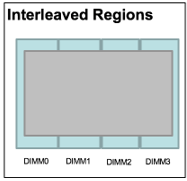
Many users choose to have one fully-interleaved set across their memory modules because this allows for increased bandwidth performance. Regions can be created or modified using the ipmctl-create-goal command, or via an option in the BIOS.
Regions can be divided up into one or more namespaces. A namespace defines a contiguously addressed range of non-volatile memory conceptually similar to a hard disk partition SCSI Logical Unit, or an NVM Express namespace. A namespace is the unit of persistent memory storage that appears in the /dev directory as a device which can be used for input and output or partitioned further. Intel recommends using the ndctl utility for creating namespaces.
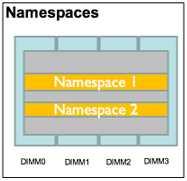
Namespaces are conceptually similar to a partition, and a label is similar to a partition table. Intel persistent memory modules support labels which allow regions to be further divided into namespaces. A label contains metadata stored on an NVDIMM.
Last updated
Was this helpful?